Lead paint once hailed for its durability and vibrant colors, now stands as a hidden hazard in millions of older homes. Predominantly used before its ban in the late 20th century, the legacy of lead paint poses serious health risks, particularly to children and pregnant women. This article delves into the prevalence of lead paint in older homes, the health implications of exposure, methods for identification and removal, and the surrounding legal framework. With an estimated 38 million homes in the United States still containing lead paint, understanding and addressing this danger is not just a matter of historical interest but a pressing public health imperative. The goal is to equip homeowners with the knowledge to identify, manage, or eliminate this toxic threat, ensuring safer living environments for all.
Contents
- 1 The Prevalence of Lead Paint in Older Homes
- 2 Health Risks Associated with Lead Exposure
- 3 Identifying Lead Paint in Your Home
- 4 Legal and Regulatory Framework
- 5 The Process of Safely Removing Lead Paint
- 6 Preventative Measures and Safe Practices
- 7 Financial Assistance and Resources
- 8 Educational Resources
- 9 The Bottom Line
The Prevalence of Lead Paint in Older Homes

Lead-based paints were extensively used in residential properties in the United States until their ban in 1978. Homes constructed before this year are likely to contain lead paint, which was favored for its quick-drying properties and durability. This historical preference means that older neighborhoods are particularly at risk, with many unaware of the lurking danger within their walls.
Despite awareness campaigns and remediation efforts, the sheer volume of affected properties presents a significant challenge. It’s estimated that a large fraction of the housing stock built before the 1980s contains some degree of lead paint. The problem is exacerbated by deteriorating paint in these aging structures, which increases the risk of lead exposure to the occupants.
Health Risks Associated with Lead Exposure
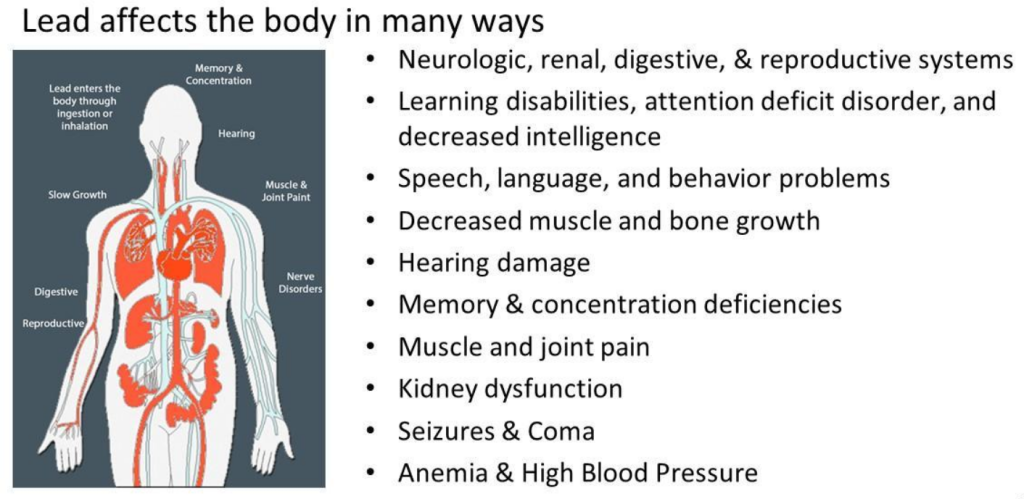
Lead is a potent neurotoxin that poses severe health risks, especially to young children and pregnant women. Short-term exposure can lead to a range of symptoms, from abdominal pain and constipation to irritability and fatigue. These immediate effects are concerning, but long-term exposure can have devastating impacts on health.
Children exposed to lead can suffer from permanent cognitive impairments, including reduced IQ, learning disabilities, and behavioral issues. For pregnant women, lead exposure can affect fetal development and result in premature birth or low birth weight. The stakes of lead poisoning underscore the critical need for vigilance and action in homes with potential lead-based paint hazards.
Identifying Lead Paint in Your Home
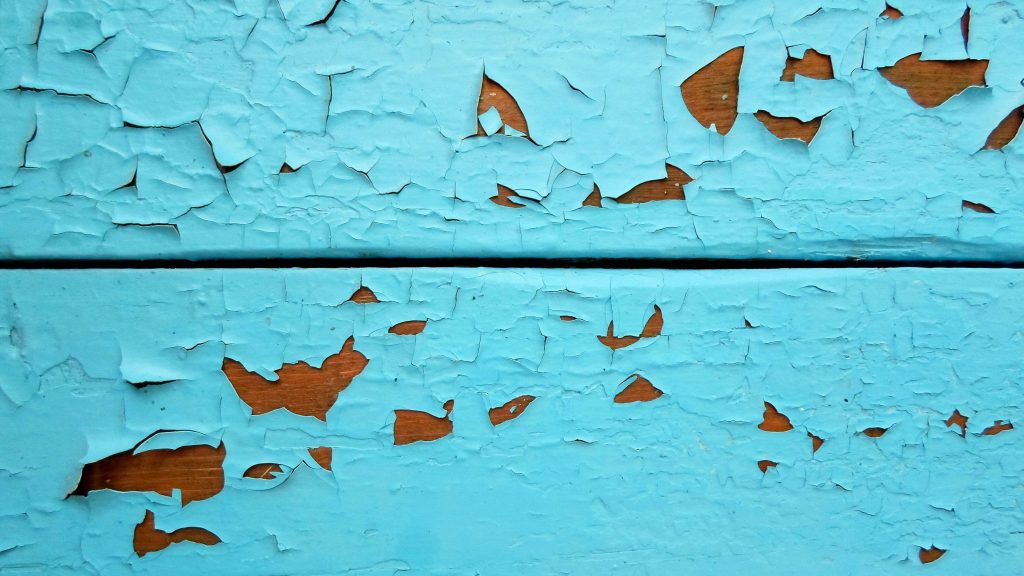

Identifying lead paint in a home is the first step toward mitigating its dangers. Lead paint often reveals itself through specific signs, such as chipping, cracking, or flaking paint, particularly on windows, doors, and trim. These visual cues can be initial indicators, but they are not definitive proof of the presence of lead.
For a conclusive identification, professional testing is recommended. This can include X-ray fluorescence (XRF) testing or taking paint chip samples for laboratory analysis. These methods provide accurate results, guiding homeowners in deciding whether lead paint remediation is necessary. Given the health risks associated with lead dust, these inspections should be conducted by certified professionals, minimizing the risk of exposure during the testing process.
Legal and Regulatory Framework

The legal landscape around lead paint in the United States mandates disclosure and remediation under certain conditions. Federal law requires sellers and landlords of properties built before 1978 to disclose any known presence of lead-based paint. This legislation informs potential buyers and tenants of the risks, allowing them to make informed decisions.
In addition to disclosure requirements, regulations guide the remediation of lead paint hazards. Certified contractors must follow strict safety protocols to prevent lead dust dispersion during removal or stabilization procedures. These regulations are enforced by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), ensuring that lead paint remediation efforts are effective and safe for workers and residents alike.
The Process of Safely Removing Lead Paint
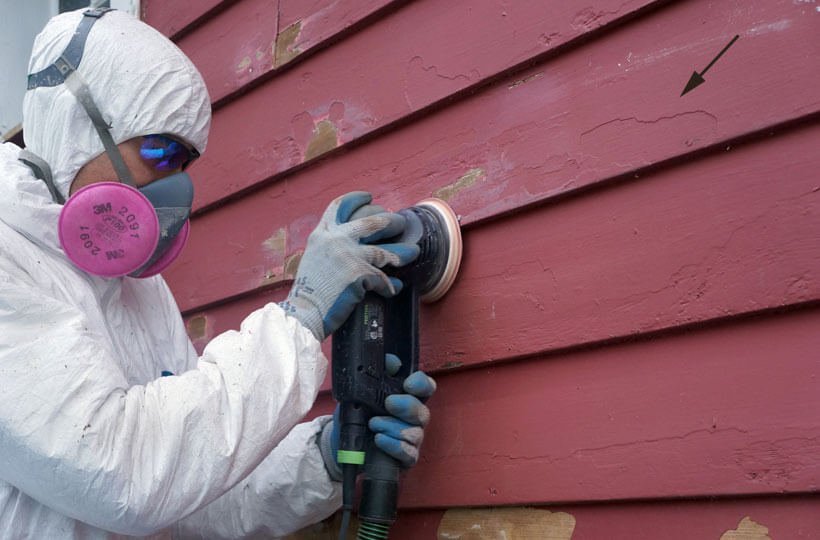

If not handled correctly, the removal of lead paint can exacerbate the hazard by dispersing toxic lead dust. DIY approaches to lead paint removal are strongly discouraged due to the high risk of exposure. Instead, hiring certified professionals who use specialized equipment and follow strict safety protocols is recommended. These experts employ methods such as wet scraping, chemical stripping, or encapsulation to remove or stabilize lead paint safely.
The process typically involves sealing off the work area to prevent contamination of the rest of the home, using HEPA-filtered vacuums to clean up lead dust, and conducting a thorough cleanup to ensure the area is safe for reoccupation. Homeowners are advised to temporarily relocate, especially if vulnerable individuals, such as children or pregnant women, are present, to minimize their risk of exposure.
Preventative Measures and Safe Practices

For homes where lead paint removal is not immediately feasible, there are measures to minimize the risk of lead exposure. Regular maintenance to keep painted surfaces in good condition can prevent paint deterioration, a major lead dust source. Homeowners can also use special sealants that encapsulate lead paint, providing a safer surface that reduces the risk of exposure.
When renovating older homes, it’s crucial to employ lead-safe work practices. This includes using protective sheeting to catch debris, employing wet sanding techniques to minimize dust, and ensuring thorough cleanup after work. Homeowners should also look for contractors certified in lead-safe work practices, as mandated by the EPA’s Renovation, Repair, and Painting (RRP) program, to ensure that renovations do not inadvertently increase the risk of lead exposure.
Financial Assistance and Resources

Navigating the financial burden of lead paint remediation can be challenging for many homeowners. Fortunately, there are resources available to help offset these costs. Federal and state programs offer grants and loans specifically designed for lead paint hazard reduction in residential properties. These programs often target low-income families or households with young children, prioritizing those most at risk from lead exposure.
Additionally, non-profit organizations and local health departments may provide educational resources, free testing kits, and sometimes financial assistance for lead paint testing and remediation. Homeowners are encouraged to explore these options, as addressing lead paint hazards improves the safety and value of a home and protects its occupants’ health and well-being.
Educational Resources

Knowledge is a powerful tool in the fight against lead exposure. Homeowners are encouraged to educate themselves about the dangers of lead paint and the best practices for managing or eliminating this risk. The EPA and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) offer comprehensive guides on identifying lead hazards, safe removal practices, and preventive measures to avoid exposure. These resources are invaluable for anyone living in or working in older homes, providing the information to navigate this complex issue safely.
Homeowners can effectively manage lead paint risks by taking advantage of educational materials and staying informed about the latest regulations and safety recommendations. This proactive approach ensures the safety of current occupants and contributes to the overall reduction of lead exposure in residential settings, benefiting communities as a whole.
The Bottom Line
The dangers of lead paint in older homes represent a significant public health concern, but they can be effectively managed with the right knowledge and resources. Homeowners can create safe and healthy living environments by understanding the prevalence of lead paint, recognizing the serious health risks, and following the recommended practices for identification, removal, and prevention. The legal and regulatory framework provides a foundation for these efforts, while financial and educational resources support those undertaking this important work. Ultimately, addressing the legacy of lead paint requires a collective effort from homeowners, communities, and government agencies, working together to protect the health and well-being of all, especially the most vulnerable among us.