The use of pesticides in modern agriculture has become a cornerstone of large-scale farming, ensuring crop protection and yield maximization. However, this widespread application has raised significant concerns about the potential health risks and environmental impacts associated with certain chemicals. While pesticides are crucial in controlling pests and diseases, their indiscriminate or uninformed use can lead to serious consequences. This post aims to shed light on some of the most harmful pesticides, delving into their uses, risks, and the growing need for public awareness and regulatory scrutiny.
Contents
- 1 Understanding Pesticides and Their Purpose
- 2 Common Pesticides and Associated Risks
- 3 Chlorpyrifos – A Neurotoxic Concern
- 4 Glyphosate and Cancer Risks
- 5 Neonicotinoids and Bee Decline
- 6 Paraquat and Lung Damage
- 7 Atrazine and Water Contamination
- 8 The Regulatory Debate Over Pesticides
- 9 Take a Stand Against Harmful Pesticides
Understanding Pesticides and Their Purpose

Pesticides are substances designed to prevent, destroy, or control pests that threaten agricultural crops and public health. These chemical agents include insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides, each targeting different types of pests. Their development and use have revolutionized farming, helping to secure food supplies by effectively managing pest populations. The role of pesticides extends beyond agriculture, contributing to disease control by eliminating vectors like mosquitoes. However, this broad utility raises questions about the implications of their omnipresence in the environment.
The history of pesticide use dates back to ancient times, but their usage escalated significantly with the advent of synthetic chemicals in the 20th century. These modern pesticides are more potent and specific in their action, offering greater efficiency in pest management. As a result, they have become integral to conventional farming practices, enabling farmers to protect crops from a myriad of pests and diseases. Nevertheless, the reliance on these powerful chemicals has led to concerns over their potential side effects, both on human health and the environment.
Common Pesticides and Associated Risks

Among the plethora of pesticides in use today, several stand out for their high usage and the risks they pose. Chemicals like Chlorpyrifos, Glyphosate, and Neonicotinoids are commonly applied in agriculture worldwide. These pesticides are praised for their effectiveness, but they are increasingly scrutinized for their potential to harm human health. Studies have linked prolonged exposure to certain pesticides with a range of health issues, including respiratory problems, neurological disorders, and even cancer.
The risks associated with these common pesticides are not uniform and can vary based on exposure levels, duration, and the individual’s health. For instance, agricultural workers who handle these chemicals regularly are at a higher risk of adverse health effects. Additionally, the persistence of these substances in the environment means they can accumulate over time, leading to long-term ecological impacts. This cumulative effect poses a significant challenge, as it can affect not just the current population but also future generations.
Chlorpyrifos – A Neurotoxic Concern

Chlorpyrifos, an organophosphate insecticide, is widely used for its efficacy in controlling a variety of agricultural pests. However, its use is controversial due to its neurotoxic properties. Studies have shown that exposure to Chlorpyrifos, particularly in children, can lead to developmental delays, learning difficulties, and other neurological impairments. This has led to a growing call for its ban or restricted use, especially in settings where children could be exposed.
Despite its known risks, Chlorpyrifos remains in use in many parts of the world, owing to its effectiveness and affordability. The pesticide works by inhibiting an enzyme essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system, which, while effective against pests, can also affect humans. The risk is particularly high during critical developmental stages, making prenatal and early childhood exposure a significant concern. The debate around Chlorpyrifos reflects the broader challenge of balancing agricultural needs with public health concerns.
Glyphosate and Cancer Risks

Glyphosate, a broad-spectrum herbicide, is perhaps best known for its association with genetically modified crops designed to be resistant to it. This allows farmers to apply the herbicide without damaging their crops, leading to its widespread use. However, Glyphosate has been at the center of a heated debate regarding its potential carcinogenic effects. The International Agency for Research on Cancer classified it as “probably carcinogenic to humans,” sparking worldwide concern and legal battles.
Despite these concerns, Glyphosate remains one of the most commonly used herbicides globally, partly due to its effectiveness in controlling a wide range of weeds. Proponents argue that when used as directed, Glyphosate is safe and plays a crucial role in modern agriculture. However, critics point to studies linking it to non-Hodgkin lymphoma and other health issues. This controversy underscores the need for rigorous, independent research to guide policy decisions and ensure public safety in the face of such widely used agricultural chemicals.
Neonicotinoids and Bee Decline
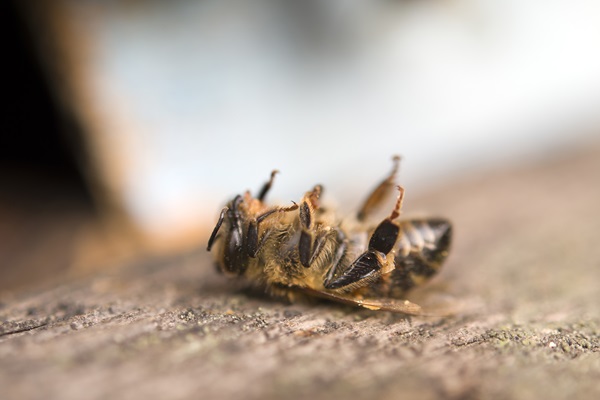

Neonicotinoids, a class of neuro-active insecticides chemically similar to nicotine, have become increasingly popular due to their effectiveness against a variety of pests. However, their impact on non-target species, particularly bees, has sparked significant environmental concerns. Bees play a crucial role in pollination, essential for the reproduction of many wild and agricultural plants. Research indicates that Neonicotinoids can disorient bees, impair their foraging abilities, and reduce their survival rates, contributing to the alarming decline in bee populations globally.
The use of Neonicotinoids is a contentious issue. While they offer farmers an effective tool for crop protection, their environmental footprint cannot be ignored. Studies have shown that these pesticides can persist in the environment, contaminating soil and water bodies and thereby affecting a wide range of organisms. The European Union has taken steps to restrict their use, reflecting a growing trend towards more sustainable and bee-friendly agricultural practices. Balancing the needs of modern agriculture with the imperative to protect essential pollinators like bees remains a significant challenge.
Paraquat and Lung Damage
Paraquat, a highly toxic herbicide, is known for its rapid action against a wide range of weeds and grasses. While its effectiveness is undisputed, Paraquat’s potential to cause serious health issues, particularly lung damage, has raised major safety concerns. Its high toxicity means that even a small amount can be lethal if ingested, and chronic exposure has been linked to the development of lung diseases, including pulmonary fibrosis. This has led to stringent regulations and even bans in several countries, though it continues to be used under strict controls in others.
The health risks associated with Paraquat are exacerbated by its persistence in the environment and the lack of an antidote. Agricultural workers and communities near treated fields are at risk of exposure through inhalation or accidental ingestion. The debate around Paraquat use often centers on the balance between agricultural efficiency and the health risks posed to workers and residents. With safer alternatives available, the continued use of Paraquat in some regions highlights the complex interplay of economic, regulatory, and health factors in agricultural pesticide use.
Atrazine and Water Contamination

Atrazine, one of the most widely used herbicides in the United States, is effective in controlling a variety of broadleaf and grassy weeds in crops like corn and sugarcane. However, its persistence and mobility in soil and water systems have raised environmental and health concerns. Atrazine is frequently detected in groundwater and surface water, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems and posing risks to human health through contaminated drinking water. Studies have linked Atrazine exposure to endocrine disruption in wildlife, affecting reproductive and developmental processes.
The use of Atrazine is a subject of ongoing debate, with environmentalists calling for tighter regulations or a ban, citing its potential to disrupt aquatic ecosystems and contaminate water supplies. In contrast, supporters argue that Atrazine is essential for effective weed control and agricultural productivity. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set limits for Atrazine in drinking water, but enforcement and monitoring remain challenging. The case of Atrazine underscores the need for a careful assessment of the environmental trade-offs involved in pesticide use, especially those that can leach into vital water resources.
The Regulatory Debate Over Pesticides

The regulation of pesticides is a complex and often contentious issue involving a delicate balance between agricultural needs, public health, and environmental protection. Different countries have varying approaches to pesticide regulation, reflecting diverse agricultural practices, economic considerations, and public health priorities. In the European Union, for instance, the precautionary principle often leads to stricter controls and bans on certain pesticides. In contrast, other countries may have more lenient regulations, prioritizing agricultural productivity and economic factors.
The debate over pesticide regulation is further complicated by the evolving nature of scientific research and public opinion. New studies can prompt a re-evaluation of the safety of certain pesticides, leading to changes in regulatory policies. However, this process is often slow and can be influenced by lobbying from the agricultural and chemical industries. Public awareness and advocacy play a critical role in pushing for stricter safety standards and more sustainable farming practices. Ultimately, the challenge lies in achieving a consensus that safeguards public health and the environment while also supporting a viable agricultural sector.
Take a Stand Against Harmful Pesticides
Awareness of the harmful pesticides discussed in this article is a crucial step toward ensuring your health and preserving the environment. As consumers, farmers, and citizens, everyone plays a pivotal role in advocating for responsible pesticide use and supporting sustainable agricultural practices. So now is the time to inform yourself, make conscious choices, and demand stricter regulatory measures. Your voice and actions can make a significant difference. When people stand together, they can foster a future where food security and environmental safety coexist harmoniously, safeguarding both the health of individuals and that of the planet.


